Understanding how a heating and cooling system works is essential when choosing the best solution for your home or business. With over 20 years in the heating and cooling industry, I’ve seen many technologies come and go, but ductless systems have gained significant popularity due to their efficiency, flexibility, and ease of installation. In this article, I’ll break down how a heating and cooling system works in general and then dive into the specifics of ductless systems, geothermal systems, and split systems to help you understand what might work best for your space.
How Does a Heating and Cooling System Work?
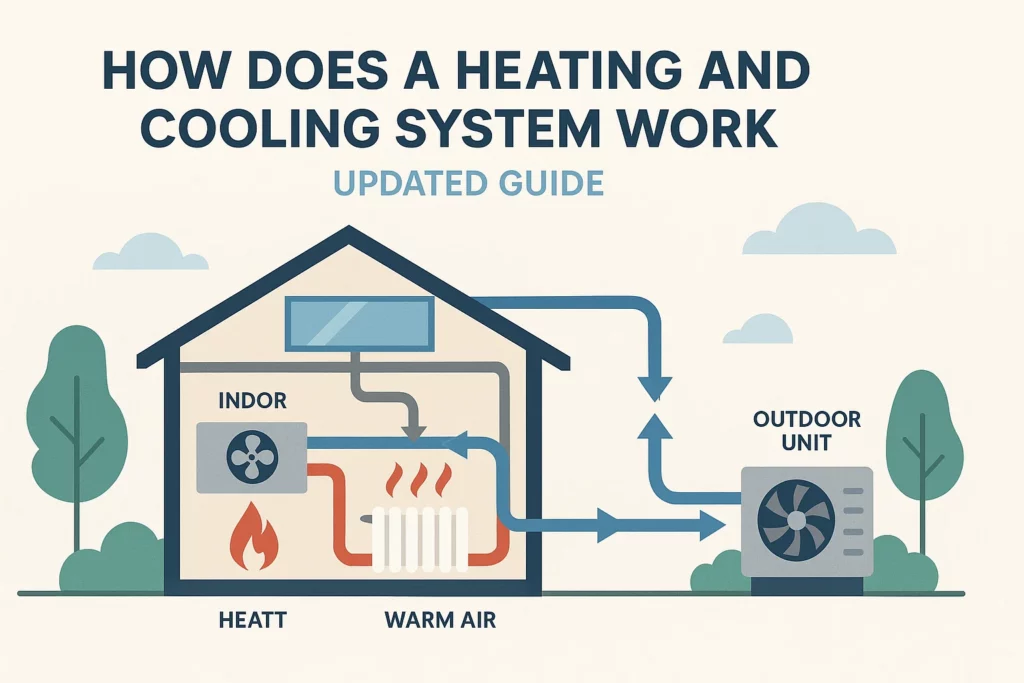
At its core, a heating and cooling system is designed to regulate indoor temperature by either adding heat to your environment during cold weather or removing heat during warm weather. These systems work by circulating conditioned air or heat through a series of components like compressors, condensers, evaporators, and fans.
Traditional systems typically rely on ductwork to distribute heated or cooled air throughout the home. The heating part may come from a furnace or heat pump, while cooling is usually provided by an air conditioner or heat pump running in reverse. Thermostats help maintain your desired temperature by signaling the system to turn on or off based on the ambient temperature.
How Does a Ductless Heating and Cooling System Work?
A ductless heating and cooling system, often called a mini-split system, works without the need for traditional ductwork. Instead, it consists of two main components: an outdoor compressor/condenser unit and one or more indoor air-handling units. These units are connected by refrigerant lines and electrical wiring.
Here’s how it functions step-by-step:
- Heat Transfer: The outdoor unit extracts heat from the air outside during the heating season or releases heat outside during the cooling season.
- Refrigerant Circulation: Refrigerant carries heat between the outdoor and indoor units through insulated copper tubes.
- Indoor Air Handling: The indoor units blow conditioned air directly into the living space, heating or cooling it as needed.
Because ductless systems bypass the need for ducts, they eliminate energy losses often associated with ductwork leakage. They also offer zoning options, allowing different rooms or areas to be controlled independently, improving comfort and efficiency.
Advantages of Ductless Heating and Cooling Systems
- Energy Efficiency: With no duct losses, ductless systems are typically more energy-efficient than traditional HVAC systems.
- Zoning: Individual control of indoor units lets you heat or cool specific rooms.
- Easy Installation: Installing a ductless system usually requires only a small hole in the wall, reducing labor and disruption.
- Flexibility: Ideal for homes without existing ductwork, room additions, or spaces like garages and workshops.
How Does a Geothermal Heating and Cooling System Work?
Geothermal systems take advantage of the earth’s stable underground temperature to provide efficient heating and cooling. Unlike air-source systems that use outside air, geothermal systems use the ground or groundwater as a heat source in winter and a heat sink in summer.
The system involves:
- Ground Loop: A series of pipes buried underground circulate a fluid that absorbs or dissipates heat.
- Heat Pump: Inside the building, a heat pump transfers heat between the ground loop and the indoor air distribution system.
- Air Distribution: Conditioned air is circulated via ductwork or radiant floor systems.
Because underground temperatures remain relatively constant year-round (around 50-60°F depending on location), geothermal systems can operate with much higher efficiency than conventional air-source systems.
Benefits of Geothermal Systems
- High Efficiency: Can reduce heating and cooling energy consumption by up to 50-70%.
- Long Lifespan: Ground loops can last over 50 years, and indoor equipment typically lasts 20-25 years.
- Environmentally Friendly: Uses renewable energy and produces minimal greenhouse gas emissions.
- Quiet Operation: No noisy outdoor compressors.
However, geothermal systems typically require higher upfront installation costs and sufficient land for the ground loops.
How Does a Split Heating and Cooling System Work?
Split systems are among the most common heating and cooling setups, featuring an outdoor unit that houses the compressor and condenser, paired with an indoor unit that contains the evaporator coil and blower.
The system works as follows:
- Outdoor Unit: Compresses refrigerant, releasing heat outside during cooling mode or absorbing heat during heating mode if it’s a heat pump.
- Indoor Unit: The evaporator coil inside cools or heats the air circulated by the blower through ductwork.
- Air Distribution: Conditioned air is pushed through ducts to various rooms.
Split systems rely on ductwork to deliver air throughout the home, so proper sealing and insulation of ducts are essential to maintain efficiency.
Choosing the Best Ductless Heating and Cooling System
When considering a ductless system, it’s important to evaluate your specific needs:
- Space Requirements: If you lack existing ductwork or want to avoid costly duct installation, ductless systems offer an excellent alternative.
- Zoning Flexibility: For homes with rooms that have different heating and cooling needs, ductless systems let you control each area separately.
- Energy Efficiency: Ductless systems typically have high SEER and HSPF ratings, translating to lower utility bills.
- Installation Costs: While initial costs can be higher than traditional systems, savings in energy and installation often justify the investment.
At High Comfort Heating & Cooling, we specialize in installing and servicing ductless systems that match your home’s layout and your comfort preferences. Our team evaluates your space, recommends the best models, and ensures proper installation for maximum performance.
How Does a Heating and Cooling System Work – Conclusion
Understanding how a heating and cooling system works—from traditional ducted setups to advanced ductless, geothermal, and split systems—empowers you to make an informed decision. Ductless heating and cooling systems stand out for their efficiency, flexibility, and ease of installation, especially in homes without ductwork or with unique zoning needs.
If you want to explore the best ductless heating and cooling options for your property, reach out to High Comfort Heating & Cooling. With two decades of industry experience, we’re here to help you achieve optimal comfort and energy savings year-round.
How Does a Ductless Heating and Cooling System Work – FAQs
What is the process of heating and cooling in USA?
The process of heating and cooling involves transferring thermal energy to regulate indoor temperatures. Heating adds warmth by generating or distributing heat, while cooling removes heat to lower temperatures, using systems like furnaces, air conditioners, or heat pumps.
What is the concept of heating and cooling system in Michigan?
In Michigan, heating and cooling systems are designed to handle extreme cold winters and hot summers, commonly using furnaces, heat pumps, and air conditioners.
Many homes use dual-fuel systems combining heat pumps and furnaces for efficient year-round comfort.
How does a residential heating system work?
A residential heating system works by generating heat through a furnace, boiler, or heat pump and distributing it throughout the home via air ducts, radiators, or underfloor pipes. It maintains indoor comfort by automatically turning on and off based on the thermostat settings.
How does the residential cooling system work step by step?
A residential cooling system works by circulating refrigerant through an indoor evaporator coil and outdoor condenser, absorbing heat from inside and releasing it outside.
The system uses a compressor, condenser, expansion valve, and evaporator to cool air, which is then distributed through ducts to lower indoor temperatures.